![]()
3.1. Amino acid sequence homology between B*2705 and
Klebsiella pneumoniae
The computer search revealed a number of sequence homol-ogies between B*2705 and various microorganisms including the nitrogenase protein of K. pneumoniae as had been reported previously by Schwimmbeck et al. [7]. The mismatch function revealed the presence of another sequence in K. pneumoniae that showed homology with the QTDRED region in B*2705. This sequence was a tetramer present in the pullulanase secretion protein pulD (residues 596-599) of a starch debranching enzyme present in K. pneumoniae (Table 1). The pulD sequence was the second amino acid homology to be identified between the hypervariable domain of B*2705 and the gram negative bacteria K. pneumoniae.
3.2. Peptide ELISA study
ELISA assays performed on the B*2705 synthetic peptide showed significant antibody elevation in AS patients in IgG (P < 0.001) antibody class, when compared to control subjects but no significant elevation in IgA or IgM antibodies. Furthermore, in the RA patients no significant elevation of IgA, IgM or IgG classes were detected when compared to controls (Fig. 1A).
Assays performed on the pulD peptide demonstrated signif-
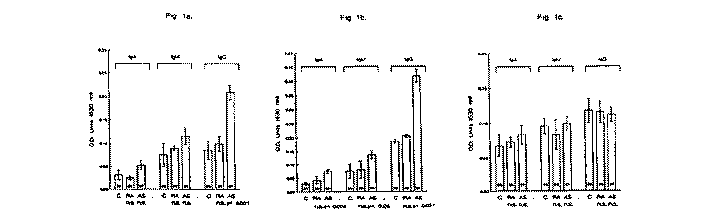
Fig. 1. Antibody litres (mean ± S.E.M.) for IgA, IgM and IgG in 25 controls (C), 25 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and 97 ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients when tested by ELISA against 16mer peptides of HLA-B27 (A), pulD (B) and control peptide (scrambled pulD) (C). OD = optical density; n.s. = not significant.
M. Fielder el al. IFEBS
Letters 369 (1995) 243-248
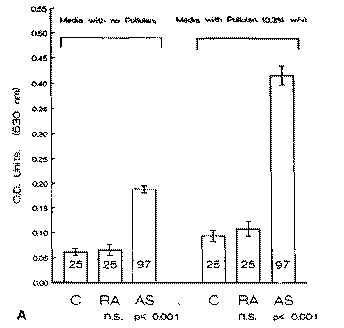
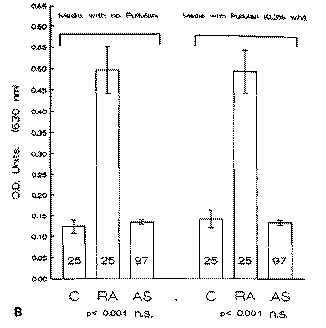
Fig. 2. Antibody litres (mean ± S.E.M.) for IgA in 25 controls (C), 25 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and 97 ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients when tested by ELISA against a clinical isolate of Klebsiella pneumonias (A) and of Proteus mirabilis (B) grown in the absence and the presence of pullulan. OD = optical density; n.s. = not significant.
leant antibody elevations in AS patients, in all three antibody classes, IgA (P < 0.005), IgM (P < 0.050) and IgG (P < 0.001) when compared to controls. The RA patients showed no significant antibody elevations in IgA, IgM or IgG classes with respect to control subjects (Fig. IB).
ELISA studies on the control peptide demonstrated no significant elevations with IgA, IgM or IgG antibody classes in RA or AS patients when compared to control subjects (Fig. 1C).
3.3. Effect of bacterial growth conditions with respect to
antibody binding
Determination of antibody levels in AS patients to K. pneu-moniae grown in minimal media with yeast extract showed elevation in IgA antibody litres (P < 0.001) when compared to controls (Fig. 2A). This observation confirms previous reports of elevation of the IgA response to K. pneumoniae in AS patients [6]. When the experiment is repeated with the addition of the starch component, pullulan (Sigma) to the medium (0.3% w/v) the level of IgA binding in AS patients was again elevated
Table 1
Comparison of amino acid sequence homologies between HLA-B27
and proteins from Klebsiella pneumoniae
Protein |
Residues |
Amino acid sequence |
HLA-B27 Klebsiella pneumoniae nitrogenase Klebsiella pneumoniae puID secretion protein |
67-S2 184-199 590-605 |
CKAKAQTDREDLRTLL CNSRQTDREDELIGGC RPTVIRDRDEYRQASS |
Regions of homology between HLA-B27, K. pneumoniae nitrogenase
enzyme and K- pneumoniae pulD secretion protein are underlined.
(P < 0.001) when compared to control subjects (Fig. 2A). This increase in the level of antibody binding is likely to be due to the development of capsular polysaccharide on the cell surface of the bacteria.
The assay was repeated using another gram negative enteric organism, Proteus mirabilis, grown under exactly the same conditions as K. pneumoniae on minimal media in the absence and presence of pullulan. Measurement of the IgG response was performed by the use of an ELISA assay. Significant and specific antibody elevations were observed in the RA patients, confirming previous observations [11]. The antibody elevations were observed in the RA patients regardless of the presence (P < 0.001) (Fig. 2B) or absence (P < 0.001) (Fig. 2B) of pullulan when compared to controls. Furthermore the levels of antibody litres in the AS, RA or control group did not appear to be affected by the presence or absence of pullulan in the growth media of P. mirabilis.
3.4. Determination of the level of serum antibodies to the
pullulanase (pulA) enzyme
Titres of both IgA and IgG antibody classes were determined by ELISA to a pullulanase target. AS patients showed litres of IgA (P < 0.001) in comparison to control subjects. The level of the IgG response showed similar elevations (P < 0.001) when compared to controls. However, the RA patients showed no significant elevalion in IgA or IgG response wilh respect to ihe control group (Fig. 3).
3.5. ELISA studies on type I and type IV collagen
IgA elevations to both type I (P
< 0.001) and type IV (P < 0.001) collagen was observed in AS
patients in comparison to controls
(Fig- 4A). IgG responses to collagen type I
M. Fielder el all FEES
Letters 369 (1995) 243-24S
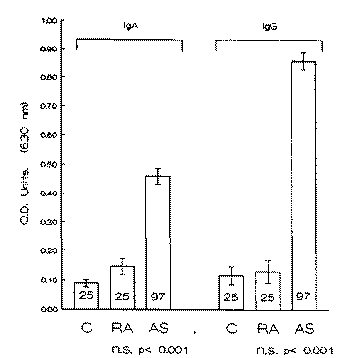
Fig. 3. Titres of IgA and IgG antibody (mean ± S.E.M.) in 25 controls (C), 25 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and 97 ankylosing spondyli-tis (AS) patients when tested by ELISA against pullulanase enzyme (pulA). OD = optical density; n.s. = not significant.
(P < 0.001) and type IV (P < 0.001) were elevated with respect to controls (Fig. 4B). The RA patients showed no significant IgA or IgG antibody elevations to type I or type IV collagen when compared to controls (Fig. 4A and B).